Product
Stainless steel fiber PFA extruded cable
Product Description
| Character | Stainless steel fiber+FPA Extruded |
| Electrical conductivity (direct current) | 8ohm-60ohm customizable |
| Flexibility / Bending Resistance | Optimal |
| High-temperature resistance | excellent(-200°C ~ +250°C) |
| Corrosion resistance | Optimal (Both conductors and insulators are resistant to corrosion) |
| Extrusion material | TPFE/FPA/FEP |
Textile inner core micro cables advantages
Stainless steel fiber PFA extruded cable usually adopts a typical 'three-layer concentric circle' structure:
1. Heating core material: stainless steel fiber bundle- Role: It is not a solid stainless steel wire, but a bundle composed of dozens or even hundreds of ultra-fine stainless steel micro-wires.
- Function: Acts as a resistive element, generating heat when current passes through it according to Joule's law (P=I²R). Its resistance value is determined by the material, diameter, number of fibers, and twisting method of the fibers.
- Advantages: - Excellent flexibility: Compared to traditional alloy heating wires like nichrome, the fiber bundle structure is very soft and can be repeatedly bent and wound without breaking easily.
- High safety: Even if individual micro-wires break due to excessive bending, the entire circuit remains conductive through other micro-wires, preventing sudden failure like a single wire, ensuring higher reliability. - Stable resistance: Corrosion-resistant, with minimal resistance variation with temperature changes.
2. Insulation layer: PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy)- Role: Insulating material wrapped outside the stainless steel fiber bundle.
- Function: Provides electrical insulation to prevent leakage and ensure safe use. It also helps shape and protect the internal heating element.
- Advantages (PFA is the core value):
- High and low temperature resistance: Long-term operating temperature can reach -200°C to 260°C, and short-term can withstand temperatures above 300°C. This is incomparable to ordinary PVC or silicone. - Corrosion resistance (chemical inertness): Can withstand almost all chemical solvents and strong acids and bases, making it ideal for use in corrosive environments.
- Low friction coefficient/non-stick: Smooth surface, preventing dirt adhesion and easy to clean.
- Excellent electrical insulation: Outstanding insulating performance.
- High transparency: PFA material is usually transparent, making it easy to observe the operation of the internal heating core.
3. Optional reinforcement/shielding layer- In higher-demand applications, an additional layer of glass fiber or extra PFA tubing may be braided outside the PFA layer to enhance mechanical strength, or a braided metal mesh (such as tinned copper mesh) may serve as a shielding layer.
Working PrincipleIts working principle is very simple: when the rated voltage is applied to both ends of the heating wire, current passes through the stainless steel fiber bundle with a fixed resistance value. Electrical energy is converted to heat, and the heat is conducted through the PFA insulation layer to the outside, heating the objects, media, or space that need to be warmed.
Finishing & coating
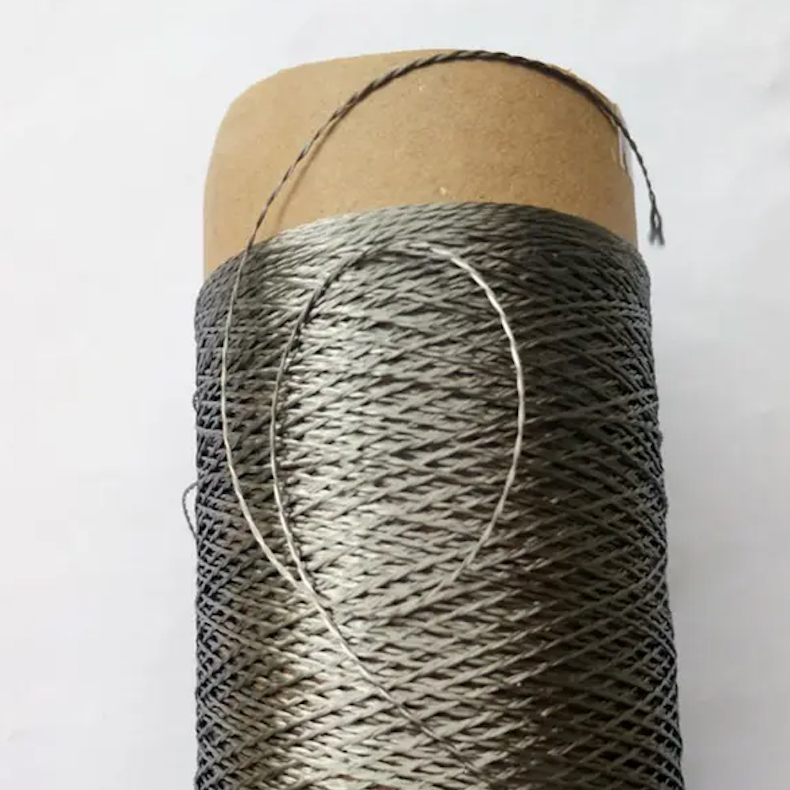

Stainless Steel Fiber Bundles
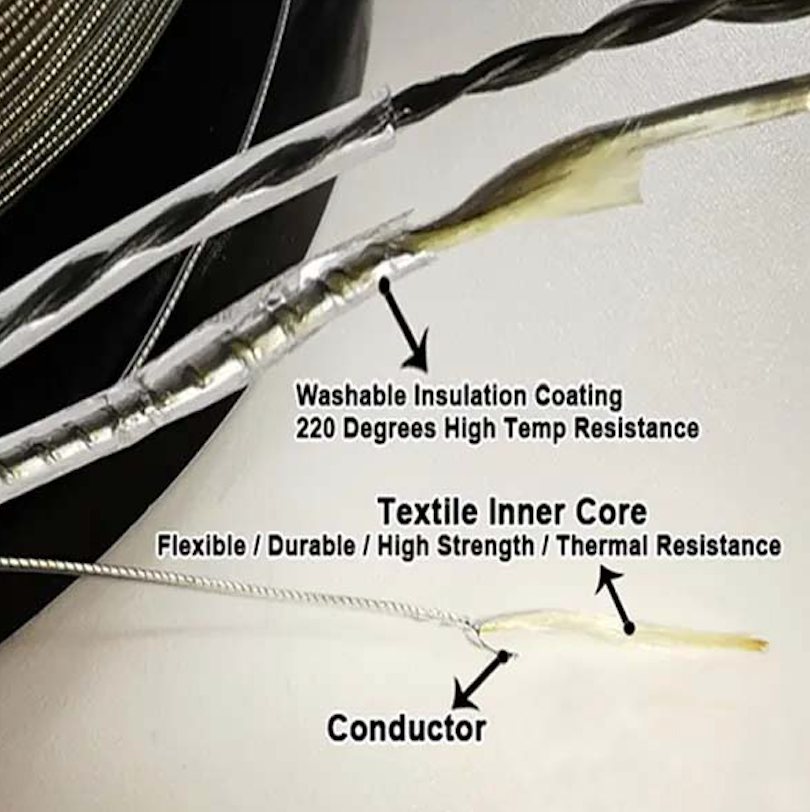
Textile Inner Core Micro Cable Constructions
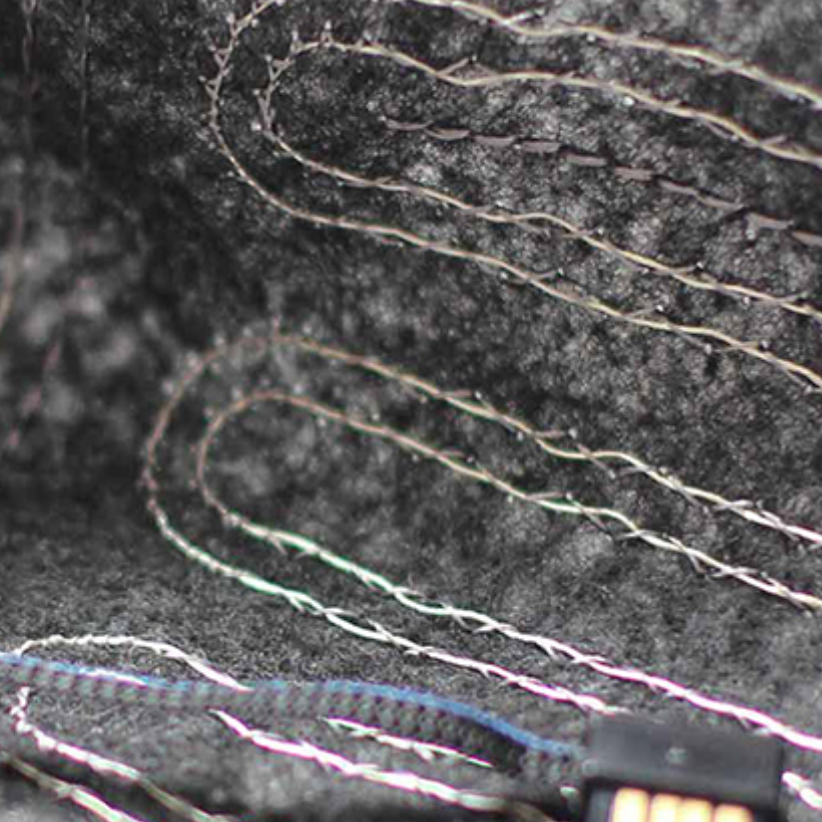

Based Embroided Heating Element
Stainless steel fiber different conductivity
|
Diameters (um) |
Filaments |
Strength (cN) |
Weight (g/m) |
Elongation (%) |
Conductivity (Ohm/ m) |
|
8 |
1000F x 1 |
69 |
0.420 |
1.10 |
16 |
|
8 |
1000F x 2 |
108 |
0.850 |
1.10 |
8 |
|
12 |
100F x 1 |
24 |
0.110 |
1.10 |
59 |
|
12 |
100F x 2 |
41 |
0.190 |
1.10 |
38 |
|
12 |
100F x 3 |
69 |
0.280 |
1.10 |
22 |
|
12 |
257F x 1 |
59 |
0.260 |
1.10 |
27 |
|
12 |
275F x 2 |
75 |
0.540 |
1.10 |
14 |
|
12 |
275F x 3 |
125 |
0.780 |
1.10 |
9 |
|
12 |
275F x 4 |
130 |
1.050 |
1.10 |
7 |
|
12 |
275F x 5 |
160 |
1.300 |
1.10 |
5 |
|
12 |
275F x 6 |
180 |
1.500 |
1.10 |
4 |
|
12 |
1000F x 1 |
100 |
0.950 |
1.10 |
7 |
|
12 |
1000F x 2 |
340 |
1.900 |
1.10 |
4 |
|
14 |
90F x 2 |
46 |
0.190 |
1.10 |
44 |
|
14 |
90F x 1 |
25 |
0.110 |
1.10 |


